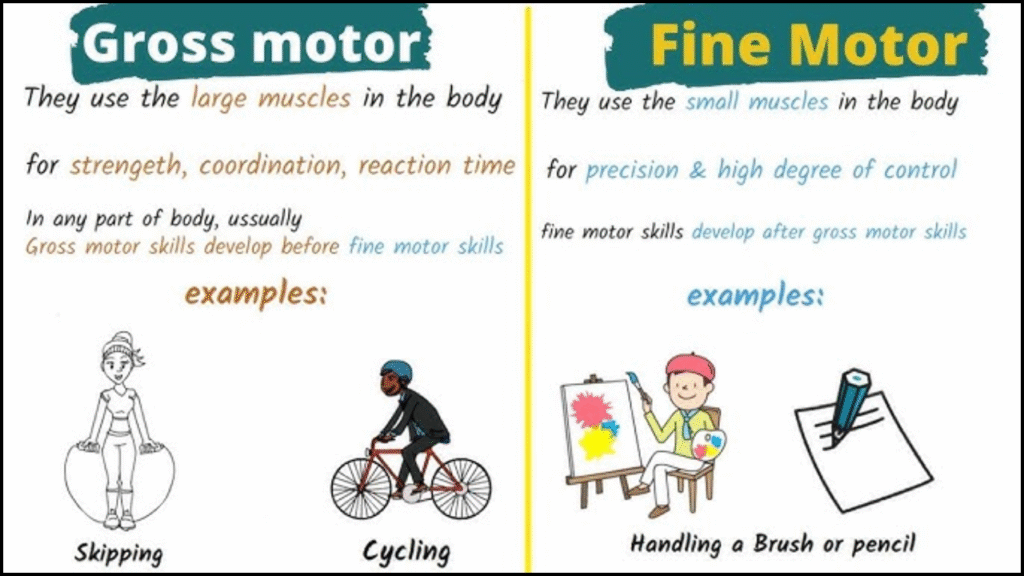
Development in children depends on many factors, and motor skills are among the most crucial. Gross and fine motor skills serve as the foundation for daily functioning and learning. Understanding the differences between them helps parents, educators, and caregivers support children more effectively. Both types are essential for physical coordination and cognitive development, but they involve different muscle groups and activities.
Table of Contents
Definition and Focus
- Gross Motor Skills: Gross motor skills involve the large muscles of the body. These include movements like walking, running, jumping, and maintaining balance. They are necessary for whole-body actions and mobility.
- Fine Motor Skills: Fine motor skills focus on small muscle groups, especially those in the hands and fingers. Tasks like writing, buttoning, and using scissors fall under this category. These skills require hand-eye coordination and concentration.
Key Differences Between Gross and Fine Motor Skills
| Aspect | Gross Motor Skills | Fine Motor Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle Groups Used | Large muscles (legs, arms, core) | Small muscles (hands, fingers, wrists) |
| Examples | Running, climbing, throwing, crawling | Drawing, typing, buttoning clothes, cutting |
| Primary Focus | Whole-body movement, strength, balance | Precision, dexterity, and hand-eye coordination |
| Development Timeline | Typically develops earlier in infancy | Usually emerges after gross motor skills mature |
| Activities Involved | Jumping, cycling, dancing | Coloring, using utensils, and zipping a bag |
| Required Coordination | Body coordination and spatial awareness | Visual-motor coordination and fine control |
| Environmental Impact | Influenced by space and physical surroundings | Influenced by available tools and structured tasks |
Developmental Milestones for Gross Motor Skills
- Infancy (0–12 months)
- Lifting head while on tummy
- Rolling over and sitting without support
- Crawling and standing with assistance
- Toddler Years (1–3 years)
- Walking independently
- Running and climbing furniture
- Kicking and throwing balls
- Preschool (3–5 years)
- Balancing on one foot
- Hopping and skipping
- Pedaling a tricycle
Developmental Milestones for Fine Motor Skills
- Infancy (0–12 months)
- Grasping toys
- Bringing hands to mouth
- Picking up small objects with the thumb and finger
- Toddler Years (1–3 years)
- Stacking blocks
- Scribbling with crayons
- Turning pages in a book
- Preschool (3–5 years)
- Drawing shapes
- Cutting with safety scissors
- Dressing with minimal help
Importance in Daily Life
- Gross Motor Skills
- Allow participation in sports and active play
- Support physical independence, such as climbing stairs or standing in line
- Contribute to confidence and social engagement during group activities
- Fine Motor Skills
- Enable writing, drawing, and other classroom activities
- Support self-care tasks such as eating and dressing
- Influence academic performance, especially in early education
Common Challenges in Development
| Type | Potential Delays |
|---|---|
| Gross Motor Skills | Trouble walking or running, frequent falls, poor balance, difficulty climbing stairs |
| Fine Motor Skills | Inability to hold a pencil correctly, messy handwriting, trouble using small objects |
Activities to Strengthen Gross Motor Skills
- Outdoor play such as tag, hopscotch, and climbing structures
- Swimming to develop whole-body strength and coordination
- Dance or martial arts to improve rhythm and controlled movement
- Obstacle courses that require crawling, jumping, and balancing
Activities to Strengthen Fine Motor Skills
- Coloring and tracing using pencils and crayons
- Stringing beads to build hand coordination
- Building with LEGO or blocks for finger strength
- Cutting and pasting to refine control and accuracy
- Using tweezers or tongs in fun sorting games
Connection to Cognitive and Social Development
- Gross motor activities enhance spatial reasoning and cooperation, especially in team-based games
- Fine motor activities contribute to early literacy, math skills (like writing numbers), and classroom participation
- Both types help boost confidence, self-regulation, and problem-solving abilities in children
Role of Caregivers and Educators
- Observation of movement patterns can detect developmental delays early
- Inclusion of both gross and fine motor exercises in daily routines enhances balanced development
- Encouragement and praise during new skill acquisition can reduce frustration and build motivation
- Adaptation of tools and environments (like using larger crayons or cushioned play areas) supports progress
Gross vs. Fine Motor Red Flags by Age
| Age Group | Gross Motor Red Flags | Fine Motor Red Flags |
|---|---|---|
| 1 year | Not crawling or standing with support | Cannot pick up small objects with the thumb and finger |
| 2 years | Cannot walk without help | Trouble stacking blocks or holding a spoon |
| 3–4 years | Falls frequently or avoids physical play | Difficulty using crayons or dressing independently |
| 5 years | Cannot hop, skip, or catch a ball | Struggles to write name or use scissors |
Professional Support for Motor Skill Delays
- Pediatricians can assess developmental progress through screenings
- Occupational therapists focus on fine motor improvement through targeted tasks
- Physical therapists help enhance gross motor strength and coordination
- Special educators may offer modified curriculum or activities for motor-impaired students
Looking Ahead
Motor skill development forms the base for many aspects of life, from physical mobility to academic performance. Gross and fine motor skills work together to support a child’s independence and success in everyday tasks. Identifying the differences between the two helps in recognizing delays, offering the right interventions, and fostering well-rounded growth.





